There are two ways of creating a bootable DOS filesystem:
The methods documented below will create a 2.88MB boot floppy (as 1.44 often hasn't enough space to hold the bios updates for modern motherboards).
DosBox
- Make sure that you have a copy of DosBox
 and a copy of a Windows 98 MS-DOS boot floppy.
and a copy of a Windows 98 MS-DOS boot floppy. - Create a directory to hold the disk images, so that you don't lose them
mkdir ~/boot cd ~/boot
- Create a blank 2.88MB floppy image and format as FAT12
dd if=/dev/zero of=floppy.img bs=1024 count=2880 mkdosfs -vvv floppy.img
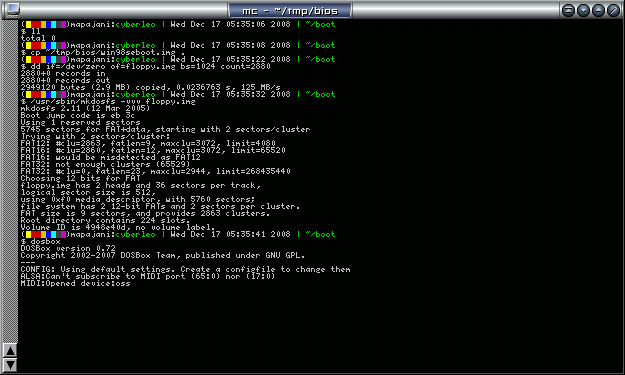
- Launch DosBox
dosbox
- Within DosBox, mount the directory containing the images, and issue a boot command to boot the Windows 98 MS-DOS boot floppy
mount c ~/boot c: boot win98s~1.img floppy.img
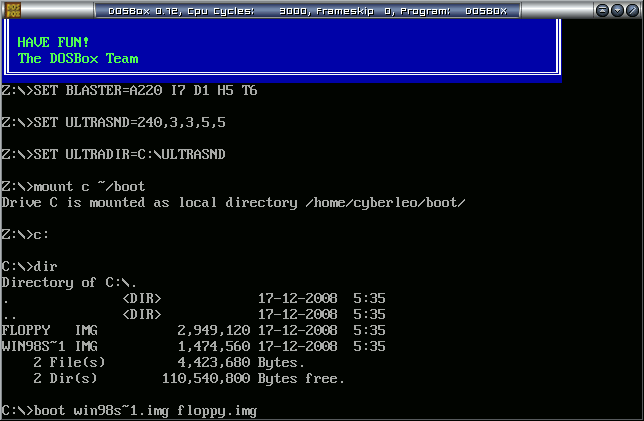
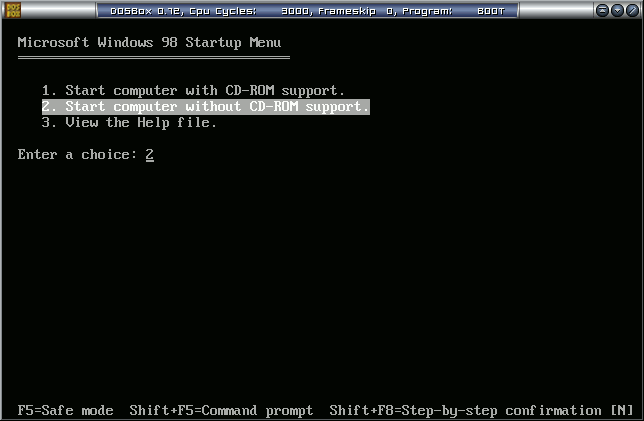
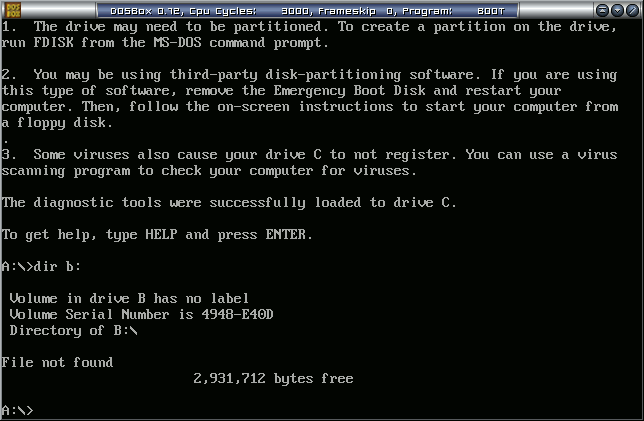
- After Windows 98 MS-DOS boots, you will be dropped to a DOS prompt. Copy the system over to the B: disk as usual
sys b:
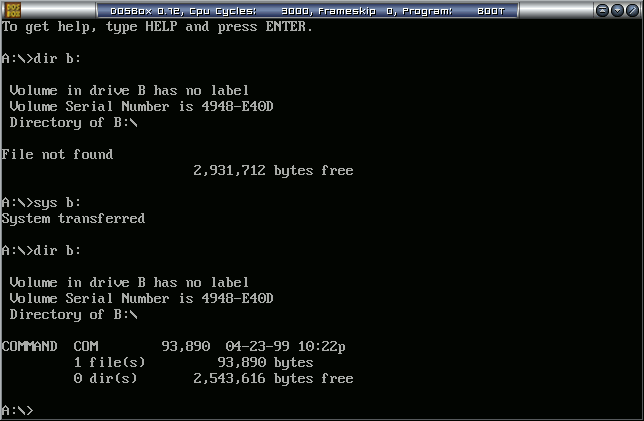
- The new disk image should now be bootable, and fully compatible with memdisk (you don't really have a real 2.88MB floppy drive lying around, do you?)
sys-freedos.pl
You will need
- mtools
- mkdosfs from dosfstools
- kernel.sys and command.com from the
 FreeDOS distribution (fdbasecd.iso:/freedos/setup/odin)
FreeDOS distribution (fdbasecd.iso:/freedos/setup/odin) sys-freedos.pl from the
 sys-freedos tarball
sys-freedos tarball- This requires perl, and probably also nasm to build the boot block
# Make a file truncate -s $(( 2880 * 1024 )) floppy.img # Add FAT12 filesystem mkdosfs -vvF12 -n DOSBOOTFLOPPY floppy.img # Copy in the FreeDOS files mcopy -i floppy.img kernel.sys command.com :: # Hide them, for consistency mattrib -i floppy.img +H +S ::kernel.sys ::command.com # Install boot block sys-freedos.pl --disk=floppy.img
- The new disk image should now be bootable
